In the ‘90s the role of HR was primarily accepted to be that of a support and an administrative one. The HR professionals focussed on activities and deliverables. The decision makers of companies also thought it to be sufficient to have them at line manager levels, and not have them involved in strategic business activities.
Globalization has forced companies to grow at a faster pace, grow business across the globe, look at optimizing all the business processes, and has even forced companies to look at strategic mergers and acquisitions.
These changes have had varying effects on all resources, most so on the "human" type. Some studies have shown that mergers and acquisitions which have failed have been primarily because of the failure in managing the human resources; either having key employees separating, or teams not able to integrate and work together as planned.
Hence, the twenty-first century has brought about the thought of seeking the involvement of HR professionals at the strategic planning level.
Further, in this era of "optimization" it was only natural to also seek optimization of the HR activities. The use of technology has brought about a revolution in the routine activities of HR. Additionally, HR outsourcing has become increasingly popular and the erstwhile back-office functions of HR are now often managed outside the company.
The role of the "old style of HR" can thus be seen as on its way to becoming extinct. If HR has to prevail, its role with external and internal stake-holders of the business has to find a way of adding value to them. HR needs to force its way into the heart of strategic planning, and organizations have to look into HR as an investment.
The Changing Business Scenario
Some of the key factors influencing change in the business scenario are as follows:-
- Globalization
- Mergers and Acquisitions
- Technology
- Outsourcing
- Workforce Demographics
Globalization
Globalization has pushed companies to grow at a faster pace. Companies are now finding that the normal growth levels of the past years are insufficient for them to survive in the face of global competition. They would now have to find ways and means to grow a lot faster. On the production front, producing goods economically is required and which is a matter of managing all resources optimally. While all other resources can be planned and managed, the "human resources" are not so easy to manage; especially when it comes to factors like effective and efficient performance.
Globalization has and will continue to diminish the influence of unions, because large multi national companies tend to be geographically mobile and cost reduction measures of outsourcing non-core activities.
Mergers and Acquisitions
In keeping with the market demands of fast growth, companies have been forced to look at strategic mergers and acquisitions. Often, these acquisitions have had to be overseas. Studies have revealed that over 85% of such acquisitions have failed to meet their strategic objectives, and the analysis has found the main reason to be the inability to effectively manage the human resources.
Technology
Innovations in technology have given a simple and new way of doing standard tasks. The application of this has resulted in automation of transaction, even in the field of HR. The major trends in technology fall in the following dimensions:-
1. Speed: things are getting faster and faster.
2. Efficiency: cost per transaction is reducing.
3. Connectivity: stakeholders are being tied closely together.
4. Customization: translate requirements into customized services.
5. e-HR: software and systems that have helped automate some of the HR processes
Outsourcing
The trend of outsourcing as a cost reduction measure is now commonplace. HR Outsourcing is no exception. Global trends indicate growth in this sector at 37% per annum. The administrative and transactional functions of HR can easily be taken care of externally at lower costs. Keeping in tune with the trend of "doing what we do best, outsource the rest" would thus see the role of HR diminishing in this area.
Workforce Demographics
The change in the way of doing business today has brought about a significant change in the workforce demographics. Some salient points that bring the role of HR in focus are as follows:-
The HR Value Proposition
Most large firms have either built service centres and invested in HR technology or outsourced these transactions. What is left after the automation, elimination, or outsourcing, is only the value proposition that HR can provide. HR must therefore necessarily deliver value to the stakeholders, like investors, customers, managers, and employees. This calls for HR transformation.
HR Transformation
Over the past decade, successful HR professionals have worked to become business partners. They have started interacting with stakeholders outside of the business as well, as they have realized the importance of getting inputs from these sources to plan their actions. They have started aligning their work with business strategies of the company, and have been trained to work in a manner that helps deliver business results.
While e-HR is a part of the overall HR transformation, it is only a way to deliver the administrative services of HR. True transformation happens when HR sees its role in delivering value to investors, customers, managers and employees. HR transformation must be more than rhetoric; it must contribute to shaping behaviour and enhancing stakeholder value.
Fundamental transformation starts with defining the HR value; who are the receivers of this value, and what will they receive.
The premise of HR value
Since vale is defined by the receiver (and not by the giver) the HR premise is that it should focus on the receivers. The HR professionals need to be open to what others want, and their perspectives. Some examples of dealing with the situation as faced across stakeholders are as follows:-
HR transformation has six important implications, which can successfully help change the way in which HR could go about their activities.
1. HR work begins with the business (not with HR).
2. The ultimate receivers of business reside in the marketplace.
3. HR strategies are a source of creating competitive advantage.
4. Align practices with requirements of the stakeholders.
5. Acquire skills required to link HR activity to stakeholder value.
6. View all the key stakeholders from a unique and powerful perspective.
The Five Elements
The HR value proposition has five elements that form an integrated HR blueprint. They are as detailed below:-
1. External business realities: like external customers, transformation of technology, economy and regulatory environments, all in the context of globalization, cause major changes in human demographics. HR actions within an organization must reflect and influence such realities.
2. Stakeholder interests: Value is defined by the receivers of the HR, more than the givers. Stakeholders are of two types.
3. HR practices: must be designed to deliver what stakeholders expect.
4. HR resources: must be organized so that individual efforts combine to create value.
5. HR professionals: must deliver value through the roles they play.
The first two determine why HR matters to an organization, while the latter three are the HR functions.
The HR value proposition
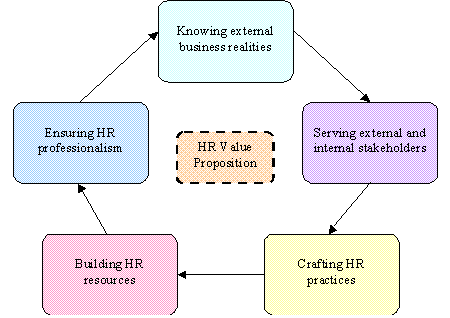
Source: Dave Ulrich and Wayne Brockbank, The HR Value Proposition, (2005), Harvard Business School Press
The fourteen criteria of the New HR
Value is the vision, elements are the goals, and the criteria are the strategies that when implemented make the HR transformation complete.
The following fourteen criteria provide the strategies and roles expected of HR.
1. Recognize external business realities, adapt HR practices, and allocate resources accordingly.
2. Create market value for investors by increasing intangibles.
3. Increase customer share by aligning with them.
4. Help line managers deliver by building organization capabilities.
5. Enhance individual abilities.
6. Manage people processes in ways that add value.
7. Manage performance in ways that add value.
8. Manage information processes in ways that add value.
9. Manage work flow in ways that add value.
10. Align HR investments with business goals.
11. Align organization with business strategy.
12. Have HR professionals play appropriate roles.
13. Have HR professionals demonstrate competencies.
14. Invest in HR professionals through training and development.
HR Competencies that matter
With the above detailed criteria in perspective, the competencies of the HR professional that matter would be as follows:-
1. Strategic Contribution
2. Personal Credibility
3. HR Delivery
4. Business Knowledge
5. HR Technology
Challenges in the Role Transformation
Transformation, or change, is always a challenge. With change to be affected across all levels of the organization, the challenge is further heightened. Some challenges are listed below:-
1. Acceptance of HR to be part of the Top Management level.
2. Knowledge and skill level of HR across other functional areas.
3. Acceptance by managers to have HR help plan workflow processes.
Conclusion
The changing business scenario, mainly driven by factors like globalization, mergers and acquisitions, technology, outsourcing, and workforce demographics, is influencing all functional areas within an organization, including HR.
Earlier HR has been playing an administrative role and was seen by the management as a support function. This support function had a cost implication and the question being raised is "what is the return on this cost?"
In the event of HR continuing to do what it had been doing, they would also be faced with a situation of whether to outsource their work, the consequence of which would be the department being shut down.
If the HR can come back with an appropriate answer that delivers value for the cost incurred, then they would not only find a place in the company, but also move on to being involved in the business of the organization.
To deliver such a value proposition, the HR team would have to undergo a transformation and deliver value as perceived by all the stakeholders of the company. The blue print to deliver this value has five elements, external business realities, stakeholder interests, HR practices, HR resources, and HR professionals, that need to work in an integrated fashion.
The fourteen criteria and the competencies required, show that there a few challenges in this transformation processes. However, these challenges need to be overcome, so that the role of HR remains. The cost optimization factor will otherwise weigh very heavily against them, particularly when compared to outsourcing options. HR must therefore deliver a value proposition.

